A) compute an accurate historical rate of return.
B) determine a stock's true current value.
C) consider compounding when estimating a rate of return.
D) determine the actual real rate of return.
E) project future rates of return.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You own 400 shares of Western Feed Mills stock valued at $51.20 per share.What is the dividend yield if your annual dividend income is $352?
A) 1.68 percent
B) 1.72 percent
C) 1.83 percent
D) 1.13 percent
E) 1.21 percent
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is defined by its mean and its standard deviation?
A) arithmetic nominal return
B) geometric real return
C) normal distribution
D) variance
E) risk premium
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The real rate of return on a stock is approximately equal to the nominal rate of return:
A) multiplied by (1 + inflation rate) .
B) plus the inflation rate.
C) minus the inflation rate.
D) divided by (1 + inflation rate) .
E) divided by (1 - inflation rate) .
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is a correct reflection of the U.S.markets for the period 1926-2010?
A) U.S.Treasury bill returns never exceeded a 9 percent return in any one year during the period.
B) U.S.Treasury bills provided a positive rate of return each and every year during the period.
C) Inflation equaled or exceeded the return on U.S.Treasury bills every year during the period.
D) Long-term government bonds outperformed U.S.Treasury bills every year during the period.
E) National deflation occurred at least once every decade during the period.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correspond to a wide frequency distribution? I.relatively low risk II.relatively low rate of return III.relatively high standard deviation IV.relatively large risk premium
A) II only
B) III only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only
E) III and IV only
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is most indicative of a totally efficient stock market?
A) extraordinary returns earned on a routine basis
B) positive net present values on stock investments over the long-term
C) zero net present values for all stock investments
D) arbitrage opportunities which develop on a routine basis
E) realizing negative returns on a routine basis
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Small-company stocks,as the term is used in the textbook,are best defined as the:
A) 500 newest corporations in the U.S.
B) firms whose stock trades OTC.
C) smallest twenty percent of the firms listed on the NYSE.
D) smallest twenty-five percent of the firms listed on NASDAQ.
E) firms whose stock is listed on NASDAQ.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the standard deviation of the following rates of return: 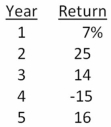
A) 10.79 percent
B) 12.60 percent
C) 13.48 percent
D) 14.42 percent
E) 15.08 percent
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the probability that small-company stocks will produce an annual return that is more than one standard deviation below the average?
A) 1.0 percent
B) 2.5 percent
C) 5.0 percent
D) 16 percent
E) 32 percent
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A stock has an expected rate of return of 13 percent and a standard deviation of 21 percent.Which one of the following best describes the probability that this stock will lose at least half of its value in any one given year?
A) 0.1 percent
B) 0.5 percent
C) 1.0 percent
D) 2.5 percent
E) 5.0 percent
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the past fifteen years,the common stock of The Flower Shoppe,Inc.has produced an arithmetic average return of 12.2 percent and a geometric average return of 11.5 percent.What is the projected return on this stock for the next five years according to Blume's formula?
A) 11.70 percent
B) 11.89 percent
C) 12.00 percent
D) 12.03 percent
E) 12.12 percent
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You've observed the following returns on Crash-n-Burn Computer's stock over the past five years: 2 percent,-12 percent,16 percent,22 percent,and 18 percent.What is the variance of these returns?
A) 0.02070
B) 0.01972
C) 0.01725
D) 0.01684
E) 0.02633
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
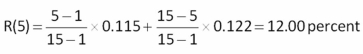 -Based on past 23 years,Westerfield Industrial Supply's common stock has yielded an arithmetic average rate of return of 10.5 percent.The geometric average return for the same period was 8.57 percent.What is the estimated return on this stock for the next 4 years according to Blume's formula?
-Based on past 23 years,Westerfield Industrial Supply's common stock has yielded an arithmetic average rate of return of 10.5 percent.The geometric average return for the same period was 8.57 percent.What is the estimated return on this stock for the next 4 years according to Blume's formula?
A) 8.70 percent
B) 8.92 percent
C) 9.13 percent
D) 9.38 percent
E) 10.24 percent
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average compound return earned per year over a multi-year period is called the _____ average return.
A) arithmetic
B) standard
C) variant
D) geometric
E) real
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following earned the highest risk premium over the period 1926-2010?
A) long-term corporate bonds
B) U.S.Treasury bills
C) small-company stocks
D) large-company stocks
E) long-term government bonds
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements concerning U.S.Treasury bills is correct for the period 1926- 2010?
A) The annual rate of return always exceeded the annual inflation rate.
B) The average risk premium was 0.7 percent.
C) The annual rate of return was always positive.
D) The average excess return was 1.1 percent.
E) The average real rate of return was zero.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Six months ago,you purchased 100 shares of stock in Global Trading at a price of $38.70 a share.The stock pays a quarterly dividend of $0.15 a share.Today,you sold all of your shares for $40.10 per share.What is the total amount of your dividend income on this investment?
A) $15
B) $30
C) $45
D) $50
E) $60
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is correct concerning market efficiency?
A) Real asset markets are more efficient than financial markets.
B) If a market is efficient,arbitrage opportunities should be common.
C) In an efficient market,some market participants will have an advantage over others.
D) A firm will generally receive a fair price when it issues new shares of stock.
E) New information will gradually be reflected in a stock's price to avoid any sudden change in the price of the stock.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct in relation to a stock investment? I.The capital gains yield can be positive,negative,or zero. II.The dividend yield can be positive,negative,or zero. III.The total return can be positive,negative,or zero. IV.Neither the dividend yield nor the total return can be negative.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I and IV only
E) IV only
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 98
Related Exams