A) Axial H atoms are directed above and below the cyclohexane ring.
B) A substitution reaction typically involves a functional group replacing a hydrogen atom on a chain or ring containing molecule.
C) A free radical is a compound with an unpaired electron.
D) LPG is linear polymerized gas.
E) Unsaturated usually means a double, triple or delocalized electron system is present in the molecule.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Give the condensed structural formula for propanone.
A) CH3COCH3
B) CH3CH2CHO
C) CH3OCH2CH3
D) CH3OCH3
E) CH3CH2CO
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does benzene have a much higher boiling point (80°C) than hexane (69°C) , even though they have the same number of carbons?
A) Benzene has fewer hydrogens than hexane.
B) Benzene is much more polar than hexane which enhances the attractive forces between molecules and raises the boiling point.
C) Benzene is planar and has delocalized electron density which increases the attractive forces between molecules and raises the boiling point.
D) Hexane has more Kekulé structures than benzene.
E) Benzene can covalently bond to another benzene molecule which increases its boiling point.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When determining the priority of substituents is "A substituent atom of higher atomic number has higher priority over a substituent atom with lower atomic number."
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
C3H8O has how many skeletal isomers?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 3
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Combustion of 493 mg of a hydrocarbon gave 1549 mg CO2 and 633.9 mg H2O. What is the molecular formula if the molecular weight is subsequently found to be 42?
A) CO2
B) CH2
C) C6H12
D) C2H2O
E) C3H6
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two simple functional groups make carboxyl group?
A) Aldehyde and keto groups
B) Aldehyde and hydroxyl groups
C) Keto and hydroxyl groups
D) Ester and hydroxyl groups
E) Ester and ether groups
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) In thermal cracking large hydrocarbon molecules are broken down into smaller molecules, ideally, molecules in the gasoline range.
B) Reforming converts straight-chain hydrocarbons into branched-chain hydrocarbons.
C) Branched-chain hydrocarbons have higher octane numbers.
D) Alkylation is the joining of small hydrocarbon fragments to larger molecules.
E) Engine knocking is caused by the smooth firing of gasoline.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures represent the structure of trans-1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To produce an organic ester, one uses a carboxylic acid and a(n) ________.
A) alkyl halide
B) alkane
C) alcohol
D) aldehyde
E) ketone
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Give the condensed structural formula for 3-bromopentane.
A) CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH2CH3
B) CH3CHBrCH2CH2CH3
C) (CH3) 3CHBrCH2CH3
D) CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH3
E) CH3CH2CBr3CH2CH3
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the rings of heterocyclic compounds we can find one or more atoms that are not carbon atoms
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following synthetic procedures are plausible? I. synthesis of esters from alcohols and acids II. synthesis of ethers from acids and alcohols III. synthesis of amides from acids and amines IV. synthesis of alcohols from alkanes and water V. synthesis of aldehydes from alcohols and oxidizing agents
A) I) , III) , and IV)
B) I) , III) , and V)
C) II) , III) , and V)
D) II) , III) , and IV)
E) III) , IV) , and V)
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many noncyclic isomers including geometric isomers of C4H8 exist?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statements regarding chiral compounds are correct? I. "Chiral carbon" is synonymous with "asymmetric carbon". II. The presence of one chiral carbon in a structure results in two possible enantiomers. III. Two enantiomers can be interconverted without breaking any bonds. IV. Two chiral molecules are mirror images of each other. V. Two chiral molecules have significantly different chemical properties.
A) II) , III) , and V)
B) I) , II) , and IV)
C) I) , III) , and IV)
D) II) , IV) and V)
E) III) , and V)
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diol, ethylene glycol, is used extensively as an antifreeze additive in automobile radiators. What properties of ethylene glycol make it a good antifreeze?
A) Ethylene glycol coats the radiator to prevent crystallization of ice at low temperatures.
B) Ethylene glycol has a higher boiling point than water and is soluble in water.
C) Ethylene glycol has a lower boiling point than water and is soluble in water.
D) Ethylene glycol forms a film on the surface of the water to prevent ice formation in the radiator.
E) Ethylene glycol will remain in the radiator after the water evaporates. This prevents freezing in cold climates.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an ethyl group is substituted for one hydrogen of cyclohexane, what would be the preferred position of that ethyl substituent on the ring?
A) axial position
B) equatorial position
C) chair position
D) boat position
E) twist boat conformation
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures represents a structure of R isomer of 1-amino-2-propanol?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following chiral compounds is(are) R enantiomer(s) ? 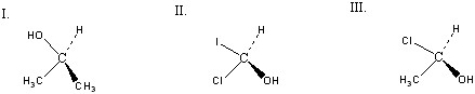
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II + III
E) I + II
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon atoms are there in the structure of 2,4,6-trimetylheptane?
A) 5 primary, 2 secondary, 2 tertiary and 1 quaternary carbon atoms
B) 5 primary, 3 secondary, 2 tertiary and 0 quaternary carbon atoms
C) 4 primary, 4 secondary, 2 tertiary and 0 quaternary carbon atoms
D) 4 primary, 2 secondary, 2 tertiary and 2 quaternary carbon atoms
E) 5 primary, 2 secondary, 3 tertiary and 0 quaternary carbon atoms
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 96
Related Exams